《水动力学研究与进展》和“Journal of Hydrodynamics”(JHD)执行编委会2018年度第二次会议于2018年4月10日(星期二)下午在中国船舶科学研究中心(702所)上海分部411会议室召开。
参加会议的有:主任委员、主编吴有生;副主任委员戴世强、林建忠、刘桦、缪国平、颜开;执行主编周连第;秘书长卢东强;执行编委槐文信、鲁传敬、马峥、潘存鸿、王道增、滕斌、吴建华、赵峰、邹早建;编辑部工作人员列席了会议。
编委会主任吴有生院士主持了会议。会议主要内容包括:
1)期刊电子出版及影响力相关汇报;
2)研讨第29届全国水动力学研讨会筹备工作;
3)研讨周培源水动力学奖有关评奖事宜;
4)研讨有关期刊发展事宜。
2017年12月,Editorial Manager系统正式运行,投稿、审稿都在EM系统进行,网址:
http://ijhd.editorialmanager.com
2018年第一期电子版于2月底正式在SpringerLink上线。网址:
https://link.springer.com/journal/42241
2018年第一期第一篇在线状态为Open Access(开放获取,即全球免费自由下载)。
3月份,第一期相继被SCI和EI收录,完成了JHD更换电子出版商后的顺利过渡。
2018年3月13日开辟了Online First专栏,标志着JHD进入快速网络化发表时代。
据Web. of Science 4月5日引文报告,
2015年论文在2017年被引137次;
2016年论文在2017年被引183次;
2017年论文在2017年被引37次。
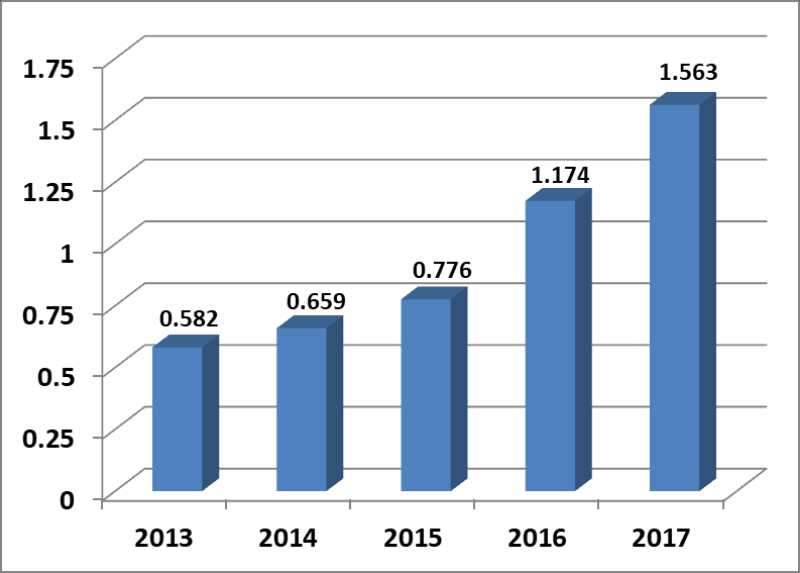
按照影响因子计算规则,据此数据JHD的2017年影响因子估算为(137+183)/(107+110)=1.475
执行主编周连第在会议和微信群里强调:“JHD 的影响因子连续两年大幅提升,从0.776(2015年)—— 1.174(2016年)—— 1.475(2017年估计)。离我们预定的八届编委会奋斗目标影响因子达1.5,进入国际SCI期刊力学类Q2区仅一步之遥。但我们在兴奋之余,尚有忧虑,尽管影响因子从1.475到1.50仅一步之遥,但路程还是很不平坦的。据估算,2018年影响因子要达到1.50,全年的引用量需达到330次,平均每月要28次,每季度84次。但据 Web of Science 4月5日检索的数据,JHD 2018年第一季度引用2016年论文39次,引用2017年论文15次,合计仅为54次。这离每季度平均84次的预定目标尚有不小差距。为此,我们向编委同仁们呼吁,我们要居安思危,不可沽名学霸王,要不忘初心,牢记使命,为实现我们的水动梦把 JHD 办成国际一流期刊而努力奋斗!”
“第29届全国水动力学研讨会”将于2018年8月24—28日在江苏镇江召开,由江苏大学承办,其中8月24日(周五)报到,25日26日学术报告。
执行编委会初步确定了大会报告8篇、分会场邀请16篇的人选。
目前已经分会场报告摘要163篇,按摘要总数排名,前几位分别为上海交通大学(28篇)、中船重工702所(17篇)、大连理工大学(16篇)、浙江大学(9篇)、中科院力学所(7篇)。
1991年,周培源基金会学术交流基金设立了“周培源优秀水动力学论文奖”,随后颁发了七届。2011年,该奖项升格为“周培源水动力学奖”,每三年评选一次。至今,该奖项已经颁发了两届(2012,2015)。
评奖秘书处简要汇报本届4位申报人情况(一位申报人中途放弃)。执行编委会讨论工作进程的安排,确定4月份投票、6月份上报周培源基金会、8月份颁奖等。
与会的执行编委进行现场无记名投票。评奖秘书处将给未出席的评委发放选票。
第13届国际水动力学会议(The 13th International Conference on Hydrodynamics, ICHD’2018)将于2018年9月2日-5日在韩国仁川松岛(Songdo, Incheon, Korea)举办,由首尔国立大学(Seoul National University)承办,Yonghwan Kim教授(ICHD执行委员)担任会议主席。
ICHD2018会议网站 http://mhl.snu.ac.kr/ichd2018
1) 发挥Online First优势,力争将论文在正式出版半年前可以网上在线发表。
2) 继续深化由被动等待型向主动进取型转型,举措包括:
(1)、开设国际会议优秀论文专栏。
(2)、开设Feature Article、Review Article栏目。
(3)、开设Letter的快车通道。
(4)、开辟重点项目快车通道专栏。
(5)、支持国家重大科研项目出产论文,组织热点交流沙龙。
前4项已经开展,第5项等待突破。
3)与其他国际会议相互支撑
(1) 第10届国际空泡会议(CAV2018)将于2018年5月14一16日在美国巴尔的摩召开,JHD副主任委员刘桦教授应邀作大会主题报告。这是中国学者第一次在这个高规格国际会议上应邀作大会主题报告,同时JHD支持下届会议在中国举办。
(2) 第13届OpenFORM会议将于2018年6月24日~29日在上海交通大学召开,JHD为此会议的联合主办单位之一,将为会议组织专家筛选论文,并从会议中遴选的优秀论文在杂志上发表。
4)继续支撑上海交通大学举办的国际暑期学校。作为联合主办单位,拟委派两名专家参加授课,同时编辑部人员将宣传推介JHD。
编辑部旧版网站运行多年,信息更新速度和界面已经跟不上时代的步伐。为此,编辑部拟在今年进行改版。
执行编委会初步预览了新版网站,并提出一些修改意见。正式的网站即将上线。
目前临时网址 http://www.jhydrodynamics.com
应集团公司关于702所下属小企业合并要求,“上海《水动力学研究与进展》杂志社”撤销,期刊业务转移至“上海中船编印社有限公司”。今后公司旗下将有《水动力学研究与进展》A辑、Journal of Hydrodynamics(B辑)、《中国造船》及《船舶力学》四本杂志运营。
目前三个编辑部拥有12名退休回聘人员,其中10名为73岁以上老专家,老龄化非常严重,同时期刊正处在转型发展时期,急需新鲜血液补充,编辑部请执行编委帮助物色合适人才:
1)、应届或往届流体力学相关专业的硕士、博士;
2)、应届或往届出版及媒体相关专业的学士(本科)、硕士;
3)、流体力学相关专业适龄的退休专家。
2018年度第二次副主编工作会议于4月10日(星期二)上午在中国船舶科学研究中心(702所)上海分部405会议室召开上午召开。参加会议的有执行主编周连第;副主编槐文信、刘桦、卢东强、马峥、滕斌、吴建华。执行主编周连第主持了会议。
会议重点讨论了:
1) 从“第29届全国水动力学研讨会”择优录取部分大会报告、分会场邀请稿件到《水动力学研究与进展》或Journal of Hydrodynamics发表。
2) 新版投稿系统Editorial Manager使用情况。
3) 制定审稿标准,规范了审稿流程;初步认可了以下审稿标准
a),一票退稿定案;
b),两个大修,原则上退稿;
c),一个大修一个录用,退回作者进行大修;
d),一个大修一个小修,退回作者进行大修。
4) 明确副主编的权限,即副主编根据审稿人的意见,(a)可以直接向作者发出退稿决定,(b)向执行主编提出录用或者小修改的决定。
4) 加快审稿程序、提高审稿质量(尤其是审稿的标准和力度)的举措。
附录: Journal of Hydrodynamics相关网址
JHD期刊信息网站: http://www.springer.com/journal/42241
JHD稿件投递网站: http://ijhd.editorialmanager.com
JHD全文下载网站:
2018-全文(国外网): https://link.springer.com/journal/42241
2006-2017全文(国外网): http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/journal/10016058
2011-2018全文(中国知网): http://www.cnki.com.cn/Journal/A-A3-SDYW.htm
《水动力学研究与进展》全文下载(中国知网):
http://www.cnki.com.cn/Journal/A-A3-SDLJ.htm
编辑部网站: http://www.jhydrod.com
ICHD秘书处网站: http://www.ichd-home.com