CONTENTS
ARTICLES
Shan-hang Chi, Chi Zhang, Ti-ti Sui, Zhu-bin Cao, Jin-hai Zheng, Jiang-shan Fan(657)
Numerical investigation of shallow wake behind a patch of rigid emergent vegetation
Jian Wang, Jing-xin Zhang, Dongfang Liang, Lian Gan(673)
Optimization of the roll motion of box-shaped hull section with anti-rolling sloshing tanks and fins in beam waves
Xin-wang Liu, Wei-wen Zhao, De-cheng Wan(688)
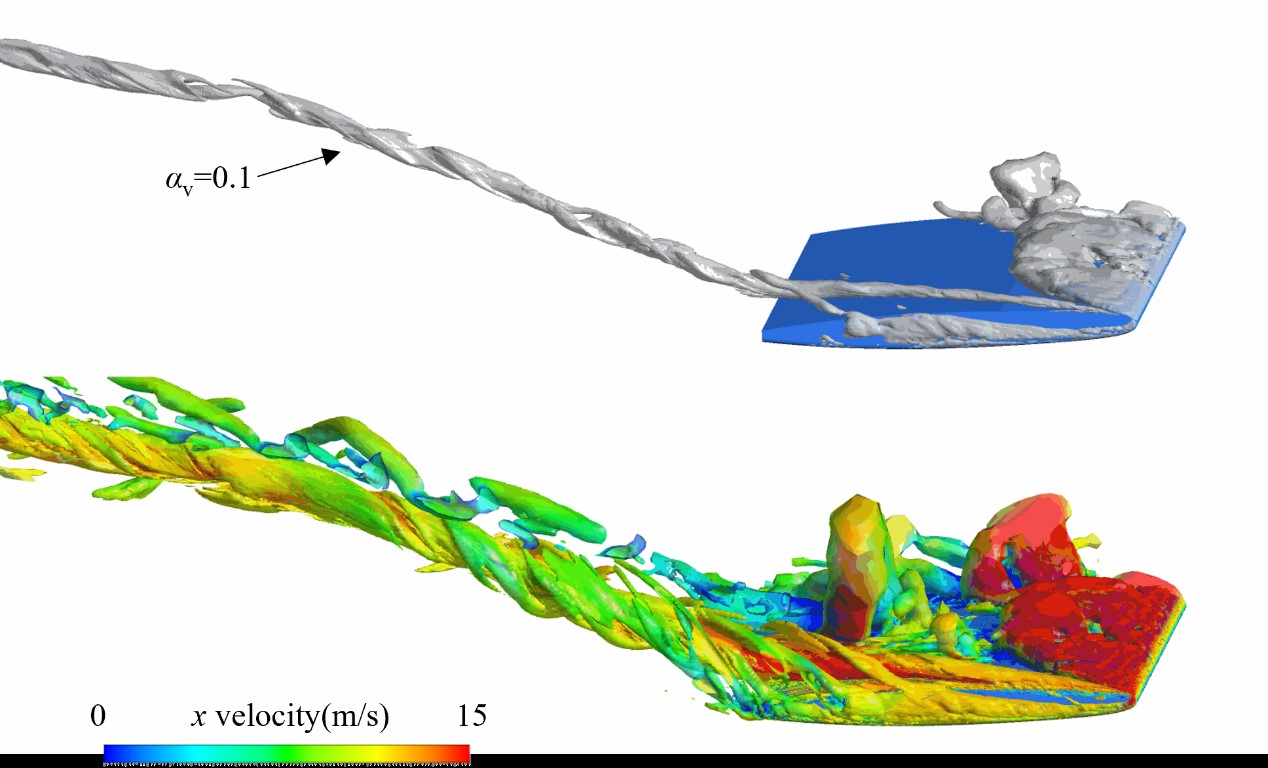
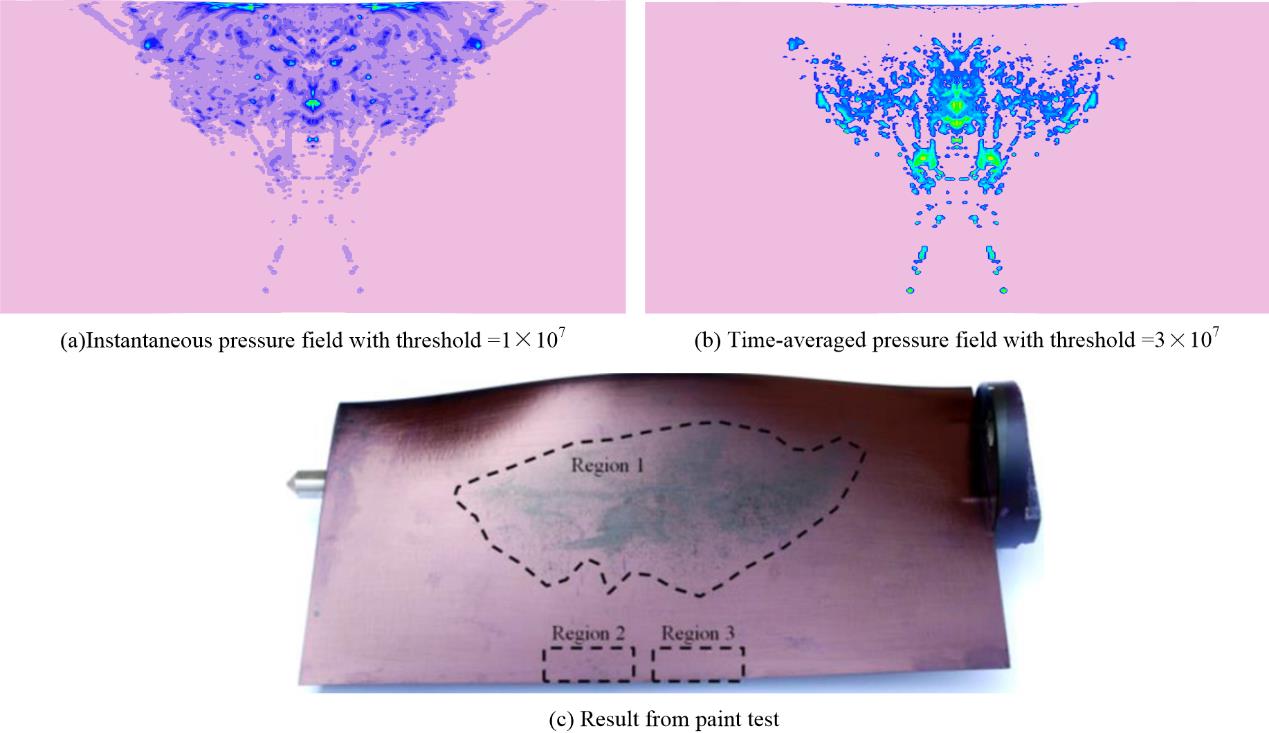
Numerical assessment of the erosion risk for cavitating twisted hydrofoil by three methods
Ting-ting Lei, Huai-yu Cheng, Bin Ji, Xiao-xing Peng(698)
The driven cavity turbulent flow with porous walls: Energy transfer, dissipation, and time-space correlations
Wen-wu Yang, Bo-fu Wang, Quan Zhou, Yu-hong Dong(712)
Evolution of the Lagrangian drift and vortex added-mass of a growing vortex ring
Shu-jia Lin, Yang Xiang, Zhuo-qi Li, Fu-xin Wang, Hong Liu(725)
Numerical investigation of the effect of T-shaped blade on the energy performance improvement of a semi-open centrifugal pump
Li-ke Wang, Jin-ling Lu, Wei-li Liao, Peng-cheng Guo, Jian-jun Feng, Xing-qi Luo,Wei Wang(736)
Computational analysis of fluid-structure interaction in case of fish swimming in the vortex street
Lang Yan, Xing-hua Chang, Nian-hua Wang, Run-yu Tian, Lai-ping Zhang, Wei Liu(747)
Influence of double-inlet design on the flow-head characteristics of axial-flow pump
Yong-sheng Zhou, Hua Zhang, Bin Chen(763)
Effects of surface roughness on overflow discharge of embankment weirs
Shang-tuo Qian, Yan Zhang, Hui Xu, Xiao-sheng Wang, Jian-gang Feng, Zhi-xiang Li(773)
An extended similarity in channel turbulence
Jiang-hua Li, Yu-xian Xia, Xiang Qiu, Yue-hong Qian, Jia-hua Li, Yuan Fu(782)
Numerical and experimental investigation of sloshing under large amplitude roll excitation
Ronja Hoch, Frank-Hendrik Wurm(787)
The hydrodynamic performance of a turbine in shallow free surface flow
Zeda Yin, Mehdi Esmaeilpour(804)
Hydroelastic analysis of water entry of deformable spheres
Liu Yang, Tie-zhi Sun, Ying-jie Wei, Cong Wang, Wei-xue Xia, Zi-lu Wang(821)
A 3-D numerical simulation of the characteristics of open channel flows with submerged rigid vegetation
Jun-tao Ren, Xue-fei Wu, Ting Zhang(833)
A non-uniform grid approach for high-resolution flood inundation simulation based on GPUs
Jun-hui Wang, Jing-ming Hou, Jia-hui Gong, Bing-yao Li, Bao-shan Shi, Min-peng Guo, Jian Shen, Peng Lu(844)
LETTERS
Chaoqun Liu(861)
Temporal and spatial characteristics of monopole acoustic energy dominated by unsteady thermodynamic cavitating flow
Xin-cheng Wang, Xiao-rui Bai, Huai-yu Cheng, Bin Ji(867)
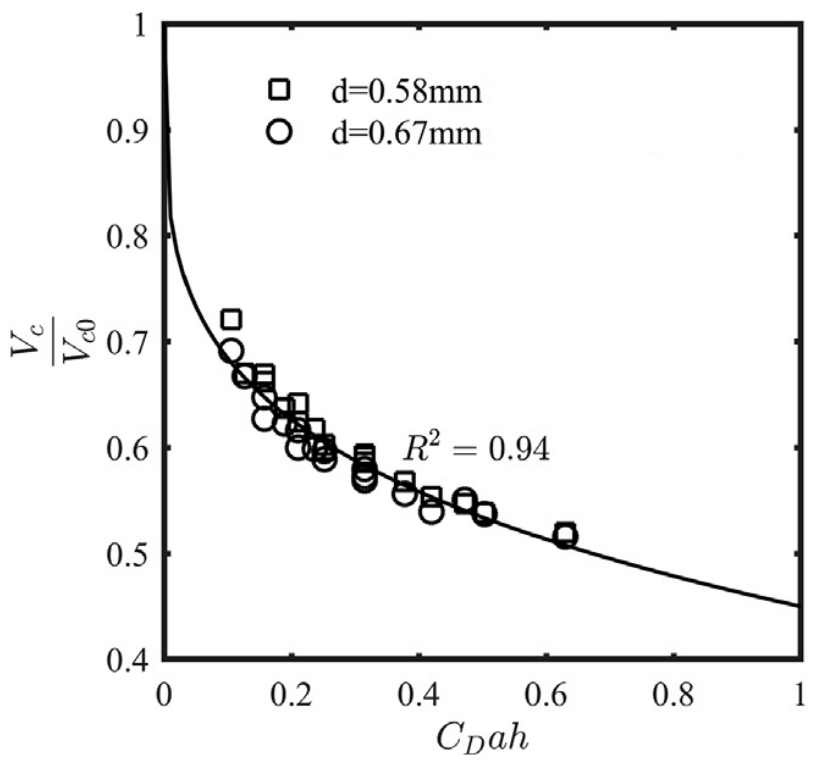
Research on theoretical and numerical methods of single bubble oscillation
Jie-min Zhan, Yue-han Chen, Yu-tian Li(872)
Editorial Message(878)